
Get to Know
Marie-Sophie Germain
Discover why we turned Marie-Sophie into a superhero
ABOUT MARIE-SOPHIE

Superhero Backstory
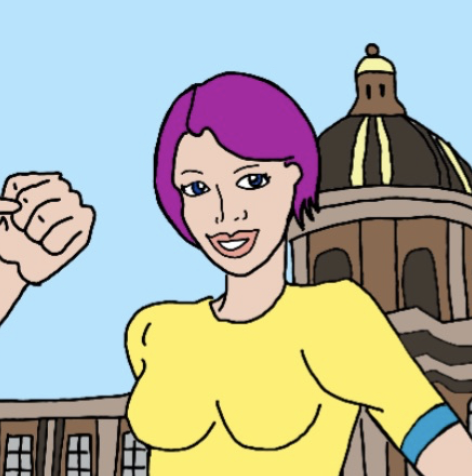
Marie-Sophie can stretch and flatten her body, like an elastic band. At times she has difficulty controlling just how elastic she makes parts of body become, this makes her very susceptible to being wounded by sharp, cutting objects.

Marie-Sophie Germain
Occupation: Computer Scientist
Born: 1776
Died: 1831
Nationality: French
Marie-Sophie was a French mathematician and one of the pioneers of elasticity theory. Born in Paris, France. When she was 13, the french revolution forced her to stay inside, to keep herself busy she turned to her father's library and became fascinated with Mathematics. It is said that at night she would wait till her parents were asleep and by candlelight do mathematics.
Marie-Sophie published her prize-winning essay in 1821, for which she won the grand prize from the Paris Academy of Sciences. The Academy of Sciences established the Sophie Germain Prize in her honour.
Born: 1776
Died: 1831
Nationality: French
Marie-Sophie was a French mathematician and one of the pioneers of elasticity theory. Born in Paris, France. When she was 13, the french revolution forced her to stay inside, to keep herself busy she turned to her father's library and became fascinated with Mathematics. It is said that at night she would wait till her parents were asleep and by candlelight do mathematics.
Marie-Sophie published her prize-winning essay in 1821, for which she won the grand prize from the Paris Academy of Sciences. The Academy of Sciences established the Sophie Germain Prize in her honour.

Did you know?
- Marie-Sophie wrote letters to Mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss under a male pseudonym. Carl only learned of her true identity when Germain, fearing for his safety during the French occupation of Hannover in 1807, asked a friend to find out where he was and ensure he was ok.
Don't miss out on additional educational resources - just scroll down the page and learn more about Marie-Sophie, Mathmematics and more.

Top Quarkz
Marie-Sophie features in our signature card game, Top Quarkz. The game supports development of maths, literacy and decision making skills all while learning about some of the most impressive scientific discoveries throughout history.
We've explained the drawing and her playing card below so you can learn more about both her superhero and her real-life identity.
We've explained the drawing and her playing card below so you can learn more about both her superhero and her real-life identity.
THE DRAWING EXPLAINED
We gave Marie-Sophie the power of Elasticity as she was one of the pioneers of elasticity theory.
The building in the background of the drawing is the Paris Academy of Sciences.
On Marie-Sophie's belt are the letters "NT". Marie-Sophie became interested in number theory in 1798. After learning more about it she started writing on number theory, and later, elasticity.
Superpower
Discovery
Marie-sophie published her prize-winning essay on Elasticity Theory in 1821.
Marie-Sophie was born in Paris, France
Location
SideKick
Hertha Ayrton was a mathematician, physicist and suffragette.
Marie-Sophie needs to be careful of sharp objects that could slice through her when she flattens herself.
Weakness
Top Quarkz Card Explained
Each drawing we create has one or more hidden treasure(s) about our superheroes' life experiences, depictions in art, jobs or discoveries. Did you find the ones hidden in this drawing?
Hidden Treasures
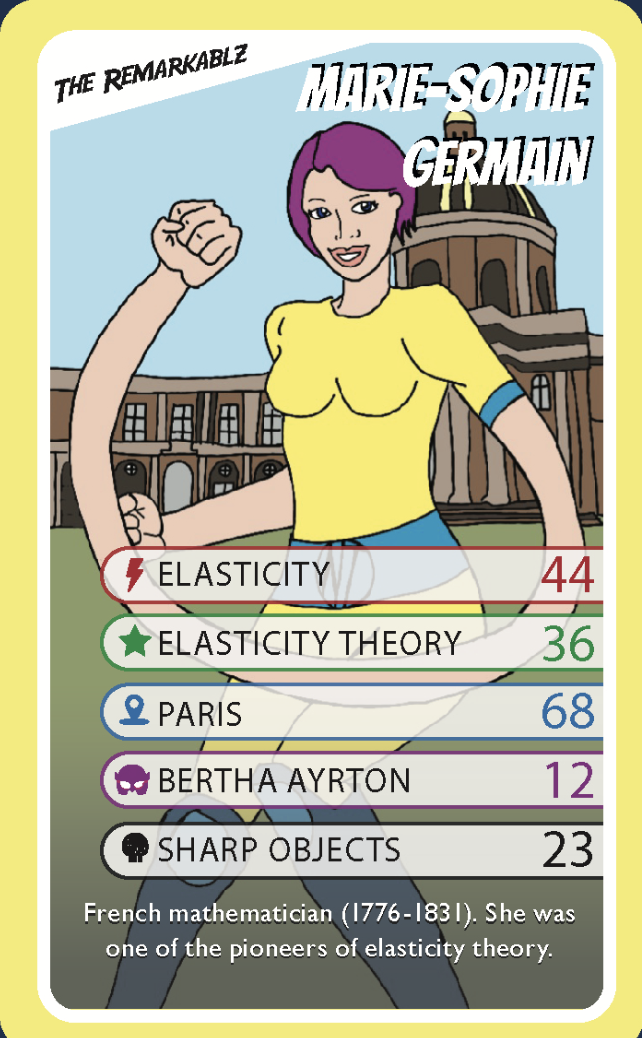
We have packed a lot into our cards - from amazing imagined superpowers to biographical information and hidden treasures.
EDUCATIONAL RESOURCES
Learn More About Marie-Sophie
Sophie Germain was a French mathematician and physicist who had to battle against the prejudices of her time to win recognition and respect.
Video Credit: discovermaths
Video Credit: discovermaths
What is Archimedes Principle?
Marie-Sophie was fascinated by Archimedes. Who was he and what is Archimedes principle?
Video credit: ScienceABC
Video credit: ScienceABC
Math is full of symbols ... here did all of these symbols come from? John David Walters shares the origins of mathematical symbols in this TedEX video.
Where do math symbols come from?
Download a Free Poster!
Download a poster of Maryam Mirzakhani. Maryam was an Iranian mathematician. She was the first woman to win the Fields Medal.
Poster Credit: Katy Alexander
Poster Credit: Katy Alexander
Sign up to our Newsletter
What Do
Mathematicians Do?
Mathematicians Do?
Mathematics is the study of numbers and how they are related to each other and to the real world. Mathematicians study mathematics either as a hobby or as a job. They apply maths in order to answer questions make discoveries.
You might not realise it but you use math every day— to cook, play games, solve a Rubik Cube... and so much more.
You might not realise it but you use math every day— to cook, play games, solve a Rubik Cube... and so much more.
DISCOVER MORE

